The 7S model, developed by Mckinsey Consulting, can describe how affectively one can organise a company, holistically. It is based around seven key elements of any organisation, with the view that in order for it to operate successfully, all the elements in this model must align synergistically together.
The factors are split into two groups: hard or soft.
The hard elements are those that can physically be seen when in place, whereas the soft are more intangible and cannot readily be seen.

7S Model can be seen below. (Notice that all elements are interrelated).
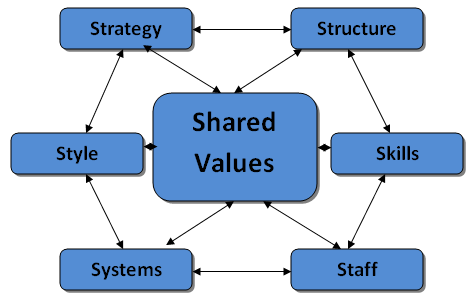
Shared values are the pinnacle of the model and therefore in any organisation. They form the underpinning culture, strategy, effectiveness and performance, linking to every other element in this framework. They link all that is of the organisation: how people behave, the structure, its systems and so on.
Getting this balance right means getting the culture right.
In addition to the Central Values alignment, each of the other six elements has an important role in designing the correct organisation and is just as important as the next.
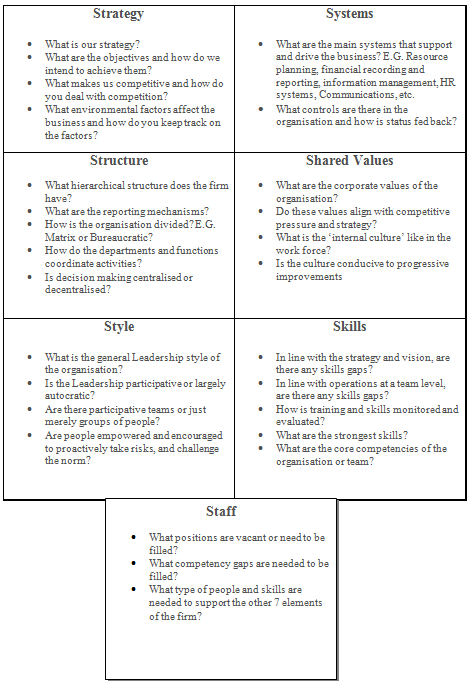
- Structure: The line of
reporting, task allocation, coordination and supervision levels - Strategy: The top level plan top create competitive advantage
- Systems: The supporting systems and process of the firm, like Information systems, financial reporting, payment systems, resource allocation etc
- Shared Values: These are the core values of the company and form the underpinning culture and how the business behaves and is perceived to behave in the wider context of the
community - Style: the overarching style of leadership adopted within the organisation
- Staff: the number and types of employees within the organisation
- Skills: the skills and competencies of the employees
Its Uses
The change agent’s task therefore, is to understand the goal of the organisation and optimise each of the seven factors in line with the corporate goals.
The framework can be used to understand where gaps may appear in the organisation, which is creating imbalance and what areas of the business to align and improve to increase performance. It can be used as a tool in a variety of corporate situations, like:
- Understanding a system change and the affects to the organisation as a whole
- Planning for a process change – A smaller change will result in a new balance of the 7S Model
- Creating Strategic and fundamental culture change
- Align departments and processes during acquisition/merger
Using the Model to Suit You
Using the 7S model, the change agent’s task is to start with the end in mind.
– That is to understand the change needed, working backwards, asking questions as to how the organisation can best be aligned across all the seven elements of the model, to achieve that objective.
Remember, this model is based around the theory that for an organisation to perform well and achieve its objectives, all seven elements must be aligned, mutually enforcing progress towards the objectives of the firm.
It comes as no surprise, therefore, that, if you understand the goal of the organisation, then the next step is to look at each element and work to realign them to create synergy.
You can use the 7S model to help analyze the current situation, a proposed future goal and then identify gaps and inconsistencies between them. It’s then a question of adjusting and tuning the elements to ensure that your organisation works effectively and well towards achieving that end goal.
Example
The following example acts as an overview to reinforce the use of the 7S model, but in reality, a more detailed analysis should be carried out for each element.
But in this example, we will look briefly at the future state of an organisation trying to drive a Lean Culture
Structure: A small hierarchy is needed, which encompasses self directed work teams. Daily interdepartmental stand up meetings to be held daily.
Systems: A bonus system which supports Lean improvement and the new ways of working, a pay grade structure that is aligned to the new team structure.
Strategy: Focus on the firm’s core competencies and deploying lean manufacturing principles throughout the firm, targeting and eliminating waste.
Skills: Develop new team skills, problem solving, waste elimination and process analysis skills, empowerment to make decisions, the ability to run and close out Kaizens
Styles: Leadership that is trained in Emotional Intelligence and the courage to delegate and empower subordinates. Leadership that leads by example and can coach and mentor employees in Lean techniques.
Staff: Team players, goal sharing, acting as change agents and driving improvements on an individual level.
Shared Values: Creating an organisation that respects each and every employee, committed to the environment and continuously strives for waste elimination and perfection in everything it does.
The 7S Model in Practice
To help with successful organisational change, the 7S Model is a good tool to use, especially in the following sequence:
1. Understand the current state – Where are we now? What is our current strategy? How are we performing?
Etc.
2. Understand the Future State – Where do you want to go? What is the strategy? How competitive will you
be?
3. Create a 7S Model review on the current state – Understand all the current elements with the
organisation at present.
4. Create a 7S Model review on the future state – What would the seven elements look like if they were
all in tandem to suit the new direction?
5. Compare the future Framework with the current state and create a plan to address the actions to fill
the gaps in each of the 7 elements.
