Much of modern day leadership thinking is based around the theory of transformational leadership, of which MacGregor Burns first introduced this concept in 1978, in his book called, ‘Leadership’.
Burns was one of the first gurus to identify that true leadership not only creates change and achieves goals within his or her environment, but changes the people and their actions for the better as well.
Imagine a time in your life, when you have been truly inspired by your boss. Perhaps you felt happy to follow his or her lead? You probably felt that the ambiance was perfect and you were empowered to learn and try new things.
Transformational leadership often provides the right make up to allow a team to flourish. It effectively takes all the leadership styles developed over the years and combines them to form one leadership theory that encapsulates leading through inspiring.
A New Dimension
Transformational Leadership was the first theory to provide an ethical and moral dimension to leadership and focuses on three main ways in which leaders transform followers:
- Increasing their awareness of task importance and value.
- Getting them to focus first on the team goals, rather than on their own interests.
- Activating their higher-order needs and truly motivating to success.
The Transformational Leader seeks to lead and drive change for the better within their teams, through leading by example; inspiring others to achieve great things; creating buy-in and motivation through self-actualisation and creating deep rooted relationships on an individual basis.
Transformational leadership also allows people to find their selves and promote leadership within the team setting, through empowerment and coaching.
Thus, the great leaders create succession planning by developing people and allowing them to take the initiative.
The Transformational Leadership Model
There are arguably a number of attributes and behaviours that exhibit a true transformational leader. These can be seen in the model below:
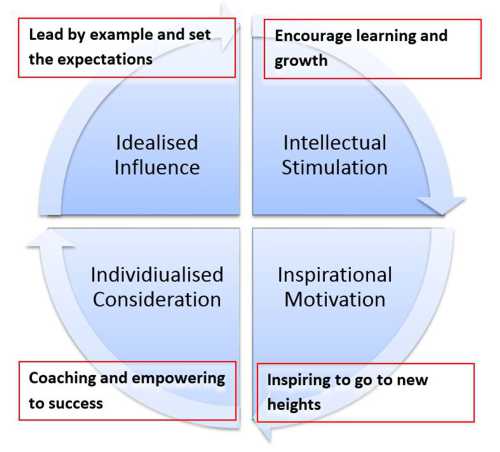
Idealised Influence –The leader acts as a role model that his / her followers seek to emulate. Through the use of demonstrating the right behaviours, they win trust and respect from their team. They also on numerous occasions, place the needs of their team and individuals first, working in an ethical and moral way. The use of power for transformational leaders is used more to influence others to achieve the team’s and their own goals.
Intellectual Stimulation – Encouraging and facilitating learning for each member of the team. This learning is more ‘learn by doing’, whereby transformational leadership encourages followers to be innovative, creative and solve problems. The team benefit through the principles of continuous improvement and trial and error, thus expanding their knowledge as they progress. They encourage new ideas from their followers and never criticise them publicly for mistakes made: the leaders focus on the “what” in problems and do not focus on finger pointing. They also easily discard an old practice set by them if it is found ineffective, in true continuous improvement style and encourage new ideas and growth through learning.
Inspirational Motivation – The aim is not punish or tell someone to do something, but inspire them to challenge the status quo. Transformational leaders guide followers by providing them with a sense of meaning and a degree of challenge. They work ardently to foster the spirit of teamwork and commitment and clearly communicate the way forward, its vision, and the objectives that the team needs to achieve. People are bought in to the idea and are brought along with the leader.
Individualised Consideration – The role of the leader here is to act as a coach and mentor, facilitating improvements, ownership, learning and empowerment. Leaders act as mentors to their followers and reward them for creativity and innovation. Team members are treated according to their skills and knowledge and in much the same way as Situational Leadership would suggest; led depending on their task ability and willingness.
People are empowered to make decisions and take on tasks that enable them to learn and develop. The leader in this respect, focuses on ensuring support is given to allow the person to succeed.
To surmise:
Think of a transformational leader as one whom:
- Leads people to situations that they have never experienced
- Gets people excited about the future and experiencing these new situations
- Enables the team to act and learn by doing through coaching and support
- Sets the example and leads the way
- Builds deep relationships on effective communication, integrity and respect
How to use the Model
- Be inspired in your heart and mind, and show it with your team. Set a goal and believe in that goal – communicate it with everyone and get people thinking about it.
- Be connected to yourself and the people around you. Be grounded in reality and understand your own values and beliefs. Learn the skill of emotional intelligence and use it to engage with your team.
- Encourage others to seek understanding themselves. Use tools like the Johari Window, Belbin Team Roles, and also Myers Briggs to help understand individual strengths and weaknesses. Use this insight to encourage development.
- Have a vision and communicate it with passion and purpose. Allow this passion and energy to inspire and motivate your team. Try to include your team in the development of goals and agree to objectives.
- Genuinely show interest and care about your team members. Take time to understand what they want, and how you can serve their interests.
- Be curious, open to new ideas and learn constantly. Use the principles of continuous improvement with your team members and encourage learning.
- Learn to coach the team and drive empowerment . Follow the steps of Flexible leadership and drive autonomy and development in tasks.
