A problem is a deviation from the standard. It is something that wasn’t expected and could be something like, poor on time delivery, poor quality, taking too long in the process, poor information flow, re-entering data in a spreadsheet, correcting a mistake, high internal scrap. It can be absolutely anything that creates an output that is not to plan.
Again, the art of being competitive in business is how quickly you can use problem solving strategies as an embedded culture, to find problems at source and eliminate them.
An alternative to PDCA, the 5 step approach is a simpler alternative, which may help a team quickly understand and try new ideas to resolve the problem at hand.
One way of solving problems is this five step method:
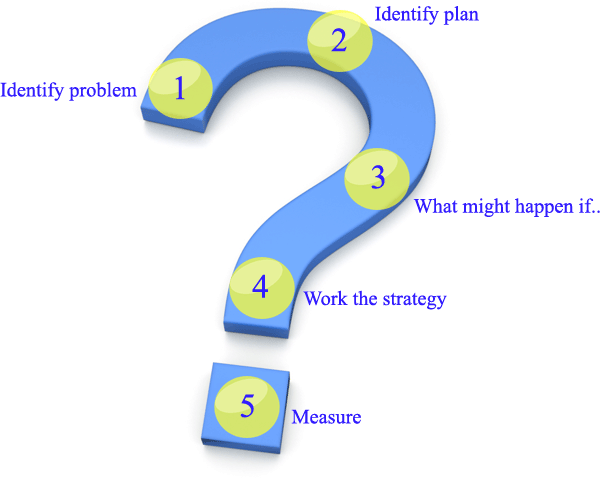
1.What is the problem?
The first stage of the 5 step problem solving model – Define exactly what the problem is.
Be clear and specific as to what exactly the problem is, when it happens, how often, what effect is it, what is the deviation from standard? See Problem statement for more information.
2. What is my plan?
Think of at least 2 or 3 possible methods that you might use to identify what went wrong. In other words, where and what do you need to investigate to help determine the cause. A strategy is a way or method or process for understanding the root causes.
3. What might happen if?
Examine your list of possible strategies from section 2, and choose the one that seems to fit best for the problem at hand.
4. Try it out!
Work the strategy, which you chose in step 3 and determine whether your team found the cause. If you did, then move onto the next step.
5. Measure
Measure the process outputs, and if the problem has gone, you are done!
If your best strategy doesn’t work, go back to your list of possible strategies in Step Two and choose another. Keep passing through the steps until your measurements tell you the problem has gone.
