Here are 5 business process improvement steps which can change the way you think about selecting process improvements in your business; and how you link them to real financial gains.
Now, the hard truth is that most businesses follow process improvement by making many small incremental gains, which often seem quite scatter gun in their nature.
And most of the time, they don’t link, or it’s hard to link them to any tangible outcome.
Firstly, there’s not really a lot wrong with making small improvements. Especially when you’re getting team buy-in, and trying to create the right behaviours.
But there’s a problem. People often start changing things for change sake. It’s hard to see the gains, but easy to see the huff and the puff of activity.
But the actual benefits of improving, normally get lost in the system.
But There’s Another Way
So wouldn’t it be great if you could link business process improvement steps to your company’s P&L management accounts?
What if you could pick the best business improvement projects by first looking at the numbers?
Then being able to clearly link every action to the bigger picture?
By doing this, you can create organisational-wide focus.
This is where the 5 Business Process Improvement Steps come into play.
It’s simple.
But don’t let its simplicity fool you.
It can be a very powerful tool to implement process improvement with great impact. And to help channel everyone’s focus.

5 Business Improvement Steps to Transform your Bottom Line.
The 5 Business Process Improvement Steps That Can Transform Your Business:
1. Analyse the health of the business through its Profit and Loss Statement
This is the first in our business process improvement steps: We need to understand profitability.
How healthy are your profits? Are gross profit margins healthy enough? What’s the net profit looking like? Is the company breaking even and barely making a profit? Are there opportunities to go after profit leaks?

Think of your business’ profitability flowing through a structure of pipes.
Where there are inefficiencies, extras costs, and delays, you incur leaks. These leaks are quite literally profitability leaks.
The more leaks, the less profit you have at the end of the pipework.
Your profitability within your Profit and Loss Account will tell you how much profitability you are retaining.
You need to get a good picture of your profitability first, before you understand what to focus on.
That’s why this is the first step in the 5 business process improvement steps to transforming your bottom line. It’s about understanding where the business is right now.
2. Drill Down to Find the Causes of the Profit Leaks
The next in our business process improvement steps is about understanding where the sources of the leaks are coming from. Some of the areas to look for are: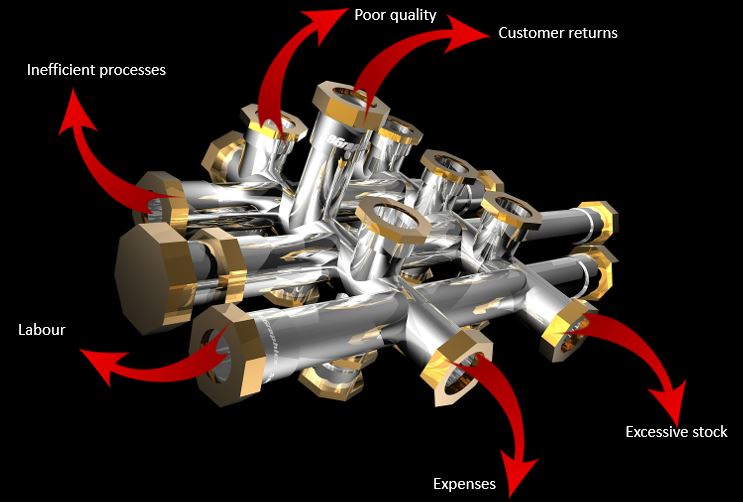
- Inefficient processes – “it should take this long but in fact it takes longer..”
- Poor quality – of information, product, service, etc
- Customer returns
- Excessive material or stock
- Excessive uncontrolled expenses
- Labour – overtime, rates, agency work
These are a just a few.
It’s important to understand the profit leaks before you begin to plan your improvements.
If you don’t have enough data, then spend time observing and understanding your profit leaks. (Discussing how to measure this is extensive and for another topic!)
3. Understand the total opportunity
When you have identified the profit leak causes, it’s time to calculate what the total opportunity the business could realise, if everything was perfect and there were no profit leaks at all.
This is fictitious, of course! Nothing can be 100% efficient, but how close can your business get to it?
And how far off is it, right now?
It can be an incredibly powerful tool to see how much losses the business is incurring.
And then to come together to see how and where they can claw as much profitability back.
4. Create an Improvement Plan
You know the health of the business – check!
You know the profit leaks and where they are – check!
You have estimated the total opportunity if everything was perfect – check!
Now it’s time to create an improvement plan to fix those profit leaks! You will now use a few lean tools to do this.
At this stage, it’s about creating one main improvement plan. One where you can get teams working together to plug the profitability leaks in the pipeline, so to speak.
5. Track the impact of your activities and make it visual
The 5 business process improvement steps would not be complete without a feedback loop. And here it is.
At this point it’s about tracking progress, and celebrating successes, too.
It’s also about ensuring the teams are on target and they’re getting the right support to realise theses improvements.
Holding regular reviews and encouraging ownership is a must. By doing this, you can encourage empowerment and leadership.
Using Visual Management – There should also be a Total Opportunities Board for all to see. This is used to track the gains made so far and provide feedback of the great work done to date.
Ask Yourself……
Is your Improvement Activity synchronised with your financial performance (P&L / Cash Flow Statement)?
- Have you captured the total improvement opportunity in one summary statement?
- Are your operational KPI’s clearly linked to the financial performance of your company?
- Too many improvement initiatives? Do you know the appropriate improvement tool to employ?
- Do your employees know how they can influence bottom line performance?
It’s All Built Around Total Opportunity
The 5 steps to business process improvement fit around the concept of “Total Opportunity.”
Here’s what I mean.
Normally, when businesses set targets, they set an allowance figure, often called a budget.
And it goes like this:
– sales target for this month is $100,000
– scrap allowance is 5%
– Productivity target is 80%
– Customer returns tolerance is 1%
– Expenses to be within 5% of budget
Now, I’m not saying that the above is terrible. What I am saying is this: what if you could open up your thinking slightly and challenge the way your business creates targets?
What if we could look at the true potential of the business before we even decide what to improve and where?
What if the world was a perfect place…. and we had no inefficiencies; no over-bloated processes, no overtime being paid out, no defects, no overruns on jobs….
If all this could disappear overnight, what could we achieve? This is the Total Opportunity.
Here’s an Example
Imagine that Saas Incorporated has a targeted yield, based on previous years’ performances of 72%.
In this example, the team actually achieve 67%.
So they are 5% down to budgeted target, which equates to $30,000 off the pace.

But if we change things up slightly………….
…………and use total opportunity; you can see 67% versus 100% potential (or total opportunity available to us).
In this example, 100% yield would equal $105,000.
Which of the two figures could inspire the teams more?
It’s a no-brainer, right?
Now, what I’m not saying is that you can suddenly achieve all of the $105,000 potential.
What I am saying is that if you can see the potential total opportunity, you can inspire teams to challenge their current working practices.
A Manufacturing Company Example
Here’s an example of the business process improvement steps for a production company.
Assuming that step 1 – interrogating the P&L had already been conducted, the team cracked on with the second step to identify the profit leaks.
In step 3, its merely about adding all the ‘potential savings together’ to find the opportunity cost.
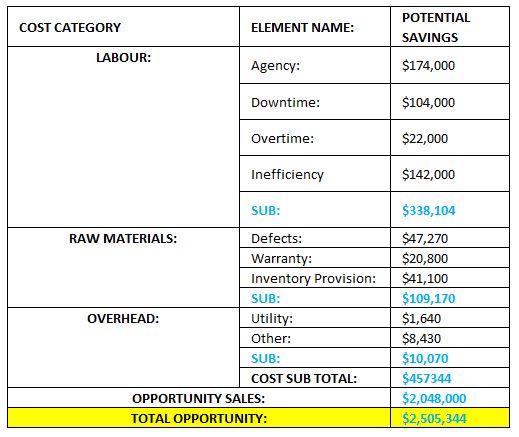
You can see a number of inefficiencies. They all add to the profit leakages of the business.
You have:
Labour Costs
– Agency workers drafted in to help meet customer demand
– Overtime – people working longer hours to help get product out the door
– Productivity losses through inefficient processes, and a difference in what should have been produced and what actually got produced.
Material Costs:
– The cost of buying the material
– The loss of material through poor process yield
– Defects
– Returns
– Warrantees
– The cost of holding inventory
Overhead Costs:
– Other costs which form the fixed costs, like utilities, subscriptions, and so on.
Sales Opportunity:
So, what’s the total opportunity in sales if everything was running 100%? Well, in this case its $2,048,000.
So, If the business didn’t have to reprocess defective parts….
If they didn’t have to worry about warrantee returns…….
If they were processing on time and doing it in an extremely productive way……
…..it would mean that the business could sell more, and this ‘selling more’ equates to an extra $2 million a year.
So adding the costs with the sales opportunity, we get $2,467,240 opportunity.
I’m sure you’ll agree, that’s pretty powerful and insightful stuff!
Now, if you were just running your business ‘to plan’ or budget, you would miss the eye-opening gold mine of the total opportunity available to you.
But this 100% can’t be achieved, I hear you say!
I know, definitely not today. And achieving 100% is probably not achievable. But how close can your business get to it? What could you achieve this year?
What could you claw back next year?
I’m sure you agree, it’s a better goal than following a budget target, that asks you to “do the same as you did last year,” or “just a little better, this time around.”
“If you shoot for the stars, then you might get to the moon.” The problem is, if you set yourself a safe goal, you’ll just stay pretty much grounded.
The business then began to direct its efforts on improving key processes. Here’s what they added to their improvement plan:
- Improving OEE (Equipment Efficiency) on their critical machines, by improving uptime, yield and setup times – this improves process lead time and the ability to get more out the door.
- Improving control of stock through Kanban supplies, and using triggers to replenish only when needed, limiting the amount of stock held at any one time.
- Improve Assembly flow of parts – increasing productivity and getting more out in the same time.
- Linking up other internal processes through a pull system and flowing product.
- Implementing a Kanban system with external suppliers to control flow and in process inventory.
The team then maintained a Total Opportunities Board to track their gains.
A Service-based Business
In this example, an MD of a window installation company analysed their Profit and Loss Account, and here’s what they found..
The owner originally wanted to talk about how to improve sales and marketing in his business. After a brief chat, it was clear that there were inefficiencies within his business, that he was unaware of.
So we took a closer look.
The business didn’t produce anything; they bought in product and fitted windows, doors and conservatories.
Here’s the simplified P&L:
We could see a number of things here:
- The business only made 33% to cover the cost of doing business for their customers
- It meant that the money left, barely covered the cost of the expenses. It was at 96% of the gross profit. – There was hardly any left in the coffers, which meant….
- $11,000 left at the end of the year from sales of $850,000!
- To top it off, the owner didn’t have enough to invest in a new service offering, that his customers were asking for.
Looking at this P&L, the first thing to see is opportunity! But where is the business leaking profitability?
Forecasted Gross Margins Were 55%
The management team couldn’t believe that gross profit was only 33%, as they always factor in 55%.
When we delved deeper, we could see that the processes that the team were working to were not controlled at all.
- More than half the jobs finished late and needed additional materials
- Staff would regularly run out of materials on site, and would have to return to get more
- The engineers’ times were checked and…….the average project overran by two days, and staff would claim overtime, on top, as well.
- The engineers would regularly plan inappropriately for the job and buy bits and pieces at the local hardware store at non-trade prices, as and when they needed them.
- Nearly every job came well below the target profit and some at a loss.

So, we put the 5 business process improvement steps to work. Here’s how:
We looked at the total opportunity if we fixed the leaks in their profitability pipework.
This came up to a tad over $1,000,000.
Imagine the transformation if we only achieved 30% of this total?
The next step was to put some process improvement tools in place to drive the cost out of the business:
- We standardised the daily planning process and provided check sheets for all Engineers to use, prior to visiting sites. They had to tick everything off, every day to ensure they had the right tools.
- We implemented a simple metric to measure the process, daily. This allowed the team to react to issues quickly. And do it before they became big problems.
- We implemented daily start up meetings, to ensure everything is going to plan and to discuss any issues that may happen or are about to happen
- Freelance contractors had their contracts changed to a fixed price, rather than by day.
From these improvements, the business managed to add $240,000 to the gross profit, which meant a net profit of $251,000.
That’s better than $11,000!
Let’s look at the process improvement tools we used to help the company:
- SOPs and checklists to standardise processes
- KPI tracking of key processes
- Daily stand up meetings
- Process mapping – to optimise the quoting process
And all it required was a bit of detailed analysis on the Profit and Loss Account…
Then finding the profit leaks, before identifying the total opportunity numbers. And then we created a process improvement plan to coordinate the projects.
Why not use this tool to drive improvements within your business?
Use the 5 business process improvement steps to link your company’s financials in with your business improvement plan.
Coordinate your teams to claw back as much opportunity as possible, using one improvement plan.
