The net result of Lean is to provide the customer with:
- What the customer wants
- When the customer wants it
- With zero defects
- At minimal cost
It’s all about Speed!
Lean Manufacturing focuses on lean principles, which aim to provide high levels of throughput, or speed.
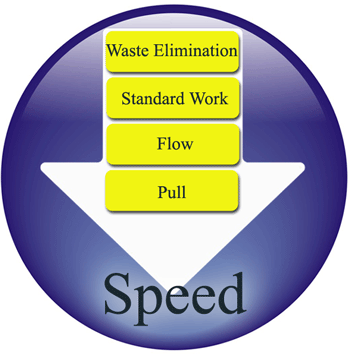 The aim is not to work faster and harder, but to worker smarter. To enable this to happen, one must focus on elimination of waste in every process; for processes to be standardised, so everyone works exactly the same way every time; making just what the customer wants, and only what he/she wants; and being able to produce only when the customer makes an order.
The aim is not to work faster and harder, but to worker smarter. To enable this to happen, one must focus on elimination of waste in every process; for processes to be standardised, so everyone works exactly the same way every time; making just what the customer wants, and only what he/she wants; and being able to produce only when the customer makes an order.
This must then be completed in a way that is efficient, which creates lean flow through the plant.
Employee Empowerment
The only way to drive a Lean philosophy across the whole organisation is to create a Lean Culture and that means engaging the workforce, and in particular, those running the processes!
This means Lean improvements are not “done to them,” but the workforce are actively involved in improvement workshops, which are commonly called a Lean-Kaizen, or Kaizen.
Through the constant pursuit of improvements by directed teams, whereby everyone is empowered, whilst learning by ‘doing’, companies can start to see big gains within their businesses, as each wasteful activity is removed or reduced.
Lean Origins
The origins of Lean emanate from The Toyota Production system (TPS) from the 1970’s, based on a vision from Mr Toyoda, to be market leader in the Automotive sector. The TPS system embraced good production practices, carried by TQM and Henry Ford, for example, but were developed furthermore to cope with today’s changing customer demands.
Concepts are constantly adopted and used and most Blue chip companies use Lean as a part of their Operating strategies to remain competitive and drive costs down.
Lean can be used not just within Manufacturing, but any business, and nowadays, many industries and sectors, including Finance, Health care and even Garden Nurseries employ lean Six Sigma to control their processes and drive waste out of their businesses.
